by Elizabeth von Pier
I’m a food lover and if you’re one too, you’ll appreciate my journey through the enchanting country of Belgium. I am on a quick three-day tour of Brussels, Dinant, Ghent and Bruges and there are plenty of opportunities to indulge my taste buds with some Belgian specialties that not only are delicious but also have an interesting history dating back hundreds of years.
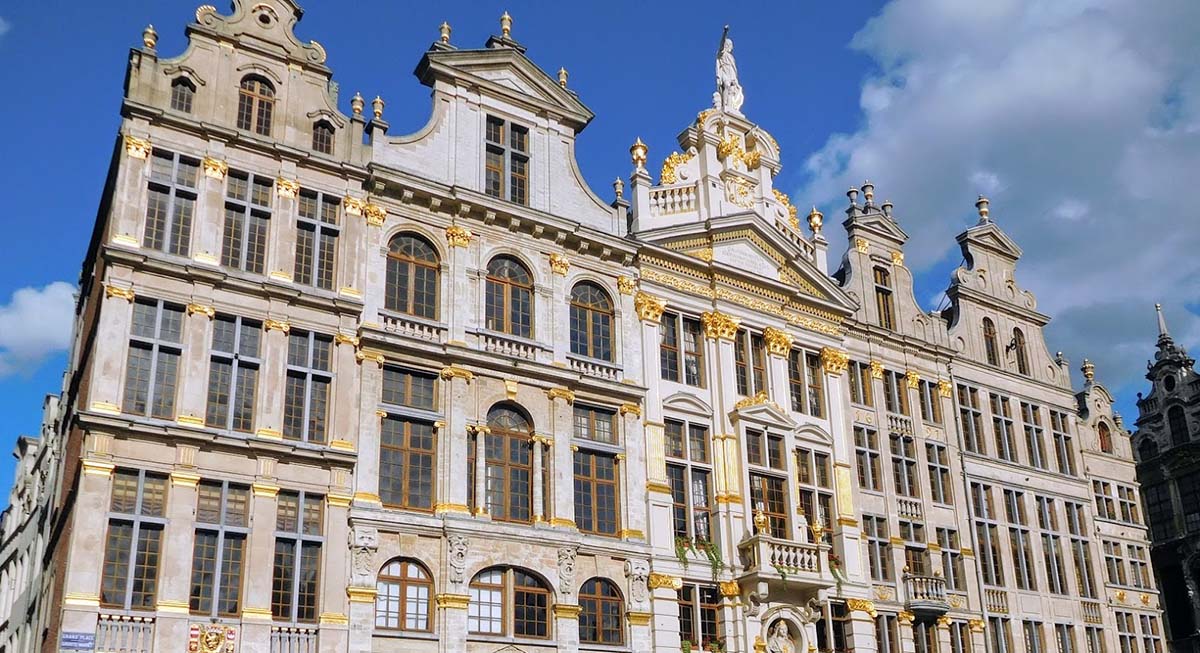
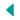
In Brussels, I start by exploring the Grand Place with its old guildhalls, Town Hall and Breadhouse building decorated with gold motifs, and make a stop to see one of the iconic symbols of Brussels, the Manneken Pis. This statue of a little boy urinating into a fountain’s basin is said to embody the Belgian spirit of independence and their sense of humor.
 I notice very quickly that there are appealing little chocolate shops on just about every street corner. No wonder. There are over 2,000 chocolatiers in Belgium and I think they all have a shop here in the capital. Famous Belgian brands that can easily be found in America include Godiva and Cote d’Or. Others like Leonidas, Nihoul, Neuhaus and Wittamer are a little harder to find stateside, but are among the best and should be tried while you’re here. Ooh, the taste, texture and smells as I wander from shop to shop testing out white, milk and dark varieties filled with various fresh-cream flavors and fashioned into tiny works of art.
I notice very quickly that there are appealing little chocolate shops on just about every street corner. No wonder. There are over 2,000 chocolatiers in Belgium and I think they all have a shop here in the capital. Famous Belgian brands that can easily be found in America include Godiva and Cote d’Or. Others like Leonidas, Nihoul, Neuhaus and Wittamer are a little harder to find stateside, but are among the best and should be tried while you’re here. Ooh, the taste, texture and smells as I wander from shop to shop testing out white, milk and dark varieties filled with various fresh-cream flavors and fashioned into tiny works of art.
Chocolate goes back centuries, to the Mayan Indians on the Yucatan Peninsula who, in 600 A.D., cured fevers and coughs using a bitter tasting drink made out of the beans that grow in pods on the trunk of the cacao tree. In the 1200’s, the Aztecs began adding flowers, vanilla and honey to enhance the flavor and in 1847, an English apothecary and doctor named Joseph Fry discovered that he could melt down the natural fat found in the cocoa bean and add it to cocoa powder to make a moldable paste which he turned into what we know today as chocolate bars. J. S. Fry & Sons was formed and later merged with and was absorbed by Cadbury’s.
 Chocolate reached its apex as an art form when in 1912 Jean Neuhaus in Brussels invented the chocolate bonbon. The chocolatier designed and sculpted beautiful confections out of the rich, smooth paste. Now, as I stand at shop windows mesmerized by the beauty of the creations, I am humored by a window displaying a three-foot tall chocolate Manneken Pis who threatens to destroy a sheet of waffles with his discharge. Inside, you can buy bags of the little guy made out of white, milk and dark chocolate and tied with a blue bow.
Chocolate reached its apex as an art form when in 1912 Jean Neuhaus in Brussels invented the chocolate bonbon. The chocolatier designed and sculpted beautiful confections out of the rich, smooth paste. Now, as I stand at shop windows mesmerized by the beauty of the creations, I am humored by a window displaying a three-foot tall chocolate Manneken Pis who threatens to destroy a sheet of waffles with his discharge. Inside, you can buy bags of the little guy made out of white, milk and dark chocolate and tied with a blue bow.
Having had my fill of sweets, I am now ready to go on to some “real” food. I start with what the Belgians call frites. They are a very popular snack here and you can find friteries with windows open to the sidewalk throughout the main pedestrianized areas of Brussels and on the squares of most Belgian towns. These are thick-cut rectangles of potato served piping hot from the fryolator in a cone you can carry with you as you walk the streets. Instead of ketchup, I eat them with the most popular accompaniment, mayonnaise, although you can buy any of twenty or so other sauces for dipping, most of them mayonnaise-based.
Be aware that the Belgians are sensitive to calling them “French fries”. They claim that they were the first to invent this dish and therefore they should be called “Belgian fries”. In fact, the name “French fries” originated during WWI when soldiers at the front were served the fried sticks and did not know if they were in France or Belgium. Someone said it was France, and thereafter they were called “French fries.”Today in Belgium, they are simply frites.
The next day I find myself in Bruges in the Flanders region where primarily Dutch is spoken. Also called the “Venice of the North”, I take a walking tour of the UNESCO-listed city with its cobbled streets and winding waterways. By now, I’ve built up an appetite for some vlaamse stoverij, the famous Flemish beef and beer stew. I’m told that a delicious version of this dish can be had at the Vivaldi Brasserie and Restaurant, so I take myself there and devour the tasty dish that is, as always in Flanders, served with a green salad and a bowl of frites. Instead of using wine in its base as the French do, here it is stewed in deep dark beer with a hint of brown sugar and cider vinegar added to give it a slightly sweet-sour taste. Along with the beef, caramelized onions and sometimes bacon are also added to the sauce.
 Of course, nothing goes better with vlaamse stoverij than one of the over 800 varieties of famous Belgian beer. Here at the Vivaldi, it is Abbey beer. I order a glass of Leffe Blond. My server Stef talks about the beer with great enthusiasm. This beer, he says, dates back to 1240 A.D. when it was made by the monks of the abbey of Notre-Dame de Leffe in southern Belgium using ingredients found in the wild. It’s a deep yellow color, strong and malty with a subtle orangey taste and a high alcohol content, and he proudly serves it in a special Leffe glass. It pairs very well with the vlaamse stoverij. I’m somewhat disappointed to learn that today it’s produced by an arm of Anheuser-Busch, although royalties are paid to the abbey for their production.
Of course, nothing goes better with vlaamse stoverij than one of the over 800 varieties of famous Belgian beer. Here at the Vivaldi, it is Abbey beer. I order a glass of Leffe Blond. My server Stef talks about the beer with great enthusiasm. This beer, he says, dates back to 1240 A.D. when it was made by the monks of the abbey of Notre-Dame de Leffe in southern Belgium using ingredients found in the wild. It’s a deep yellow color, strong and malty with a subtle orangey taste and a high alcohol content, and he proudly serves it in a special Leffe glass. It pairs very well with the vlaamse stoverij. I’m somewhat disappointed to learn that today it’s produced by an arm of Anheuser-Busch, although royalties are paid to the abbey for their production.
I’m now ready for some dessert and nothing is more enticing than Belgian waffles. This is a very popular indulgence in the evening. Like frites, Belgian waffles are made in little waffle stands throughout the pedestrianized areas of most cities and towns and are served with a fork and a special waffle holder. Emilie makes one for me using a waffle iron and corrects me—here they are called simply “waffles”, not Belgian waffles. She offers a choice from a variety of toppings including whipped cream, icing sauce, butter, pistachios, candy sprinkles, shaved chocolate, coconut, banana, fresh strawberries, Nutella and drizzles of chocolate, caramel, or strawberry sauce.
 We talk as she pours the batter into the maker, creates a crispy brown beauty, and adorns it with fresh strawberries, whipped cream and chocolate drizzle. Learning that I’m from America, she tells the story of how Belgian waffles were introduced, first as the Brussels Waffle in 1958 at an expo in Bruxelles. A few years later, Maurice Vermersch opened a stand in the Belgian Village at the 1964 World’s Fair in Flushing Meadows, New York where he sold them covered with strawberries and whipped cream. But Maurice found that most people in the U.S. did not know that Brussels was the capital of Belgium, so he named them Bel-Gem Waffles, a play on words, which later morphed into Belgian Waffles. The concoction became very popular and they have since taken off in the U.S. Emilie and I laugh together as she hands me my “Bel-Gem waffle”.
We talk as she pours the batter into the maker, creates a crispy brown beauty, and adorns it with fresh strawberries, whipped cream and chocolate drizzle. Learning that I’m from America, she tells the story of how Belgian waffles were introduced, first as the Brussels Waffle in 1958 at an expo in Bruxelles. A few years later, Maurice Vermersch opened a stand in the Belgian Village at the 1964 World’s Fair in Flushing Meadows, New York where he sold them covered with strawberries and whipped cream. But Maurice found that most people in the U.S. did not know that Brussels was the capital of Belgium, so he named them Bel-Gem Waffles, a play on words, which later morphed into Belgian Waffles. The concoction became very popular and they have since taken off in the U.S. Emilie and I laugh together as she hands me my “Bel-Gem waffle”.
The waffles in Belgium are larger, fluffier and with deeper squares than those in the U.S. This is because the batter is raised with yeast and egg whites are folded in, rather than baking powder as in the U.S.
The next day I find myself in Dinant, Belgium, the birthplace of the inventor of the saxophone, Adolphe Sax. Saxophones decorate the streets of Dinant, painted with modern art designs on the bridge over the River Meuse, on the lampposts, and in the special museum devoted to Mr. Sax.
But I pass up the museum to go to the little family-run shop on rue Grande which makes cocques. Pronounced “kooks”, these are an interesting and unusual confection made only in this shop. The windows draw you in with their beautiful displays of what look like gingerbread cookies formed into an assortment of lovely designs depicting flowers, animals, people and landscapes.
Cocques date from the 15th century when Charles the Bold besieged the town and left no food except for honey and flour. The industrious residents found a way to create a tasty concoction from these two ingredients. Today a little sugar is added to the recipe and the dough is pressed into molds made by local metalcrafters and baked. On cooling, they become rock hard and can be preserved indefinitely as long as they are kept dry. Tourists buy cocques all year long, but Belgians typically indulge in them around St. Nicolas day in the winter.
One of the Jacobs family explains how to eat them and warns against biting off a piece of the cocque because it will break your teeth. She says that the local dentist is a very rich man from repairing teeth for cocque eaters. She recommends using a hammer on a very hard surface—like cement—to break them into bite-sized fragments. Then you suck on the pieces and leave them to melt in your mouth until they are soft and chewy. You might also leave them to soak in coffee, but since they are so hard, it will take quite some time for them to soften, even in the hot liquid.
Stock up on this unique and tasty treat since you won’t find it anywhere else in the world.
If You Go:
Cocques at Patisserie Jacobs, Rue Grande 147, 5500 Dinant (00 32 82 22 21 39)
Leonidas, 17 Rue des Fripiers/Kleerkopersstraat 17, 1000 Brussels, for great chocolates (many other shops throughout the city and major towns)
Vivaldi Brasserie, Wijngaardstraat 24, 8000 Bruges
About the author:
Elizabeth von Pier is a retired banker and an avid traveler, photographer and writer. She has been published in the Los Angeles Times, In the Know Traveler, Go Nomad, Wave Journey, Hackwriters, Travelmag—The Independent Spirit, and Travel Thru History, and recently published her first book, “Where to Find Peace and Quiet in London.” Ms. Von Pier lives in Hingham, Massachusetts.
Photos by Elizabeth von Pier






 The real heart of the city is the bustling Piazza della Sala, which dates from the 12th century. The characteristic well, “Il Pozzo del Leoncino” (Well of the Little Lion), makes an impressive centre piece to this charming square, which hosts a daily fruit and vegetable market and is surrounded by tiny shops brimming with Tuscan delicacies such as cheese, fresh pasta, delicious bread and a variety of meat products. Lining the square are numerous bars and restaurants, which form the hub of the “movida Pistoiese” and attract hundreds of people of all ages in the evenings, particularly in summer.
The real heart of the city is the bustling Piazza della Sala, which dates from the 12th century. The characteristic well, “Il Pozzo del Leoncino” (Well of the Little Lion), makes an impressive centre piece to this charming square, which hosts a daily fruit and vegetable market and is surrounded by tiny shops brimming with Tuscan delicacies such as cheese, fresh pasta, delicious bread and a variety of meat products. Lining the square are numerous bars and restaurants, which form the hub of the “movida Pistoiese” and attract hundreds of people of all ages in the evenings, particularly in summer. Apart from typical Tuscan attractions including splendid striped churches, ancient city walls and the fortress of Santa Barbara, built by the Florentines in 1331, Pistoia also has some more unusual monuments. The ancient hospital, dating form the 13th century, features an unmissable glazed ceramic frieze created by various artists, including Giovanni Della Robbia, which depicts the seven works of mercy. Underneath the hospital itself, you can follow a fascinating itinerary where you can see artefacts used by plague victims, an ancient laundry and olive oil mill and finally end up in the smallest anatomical theatre in the world.
Apart from typical Tuscan attractions including splendid striped churches, ancient city walls and the fortress of Santa Barbara, built by the Florentines in 1331, Pistoia also has some more unusual monuments. The ancient hospital, dating form the 13th century, features an unmissable glazed ceramic frieze created by various artists, including Giovanni Della Robbia, which depicts the seven works of mercy. Underneath the hospital itself, you can follow a fascinating itinerary where you can see artefacts used by plague victims, an ancient laundry and olive oil mill and finally end up in the smallest anatomical theatre in the world. Pistoia really comes to life in the summer and hosts The Pistoia Blues Festival in July, where artists such as B.B. King, Buddy Guy, Bob Dylan, Lou Reed and David Bowie have played. The 25th July is the feast of the town’s patron St James, and the streets fill up with a medieval procession displaying stunning costumes, flag waving and music, which culminates in a jousting tournament in Piazza del’ Duomo.
Pistoia really comes to life in the summer and hosts The Pistoia Blues Festival in July, where artists such as B.B. King, Buddy Guy, Bob Dylan, Lou Reed and David Bowie have played. The 25th July is the feast of the town’s patron St James, and the streets fill up with a medieval procession displaying stunning costumes, flag waving and music, which culminates in a jousting tournament in Piazza del’ Duomo.
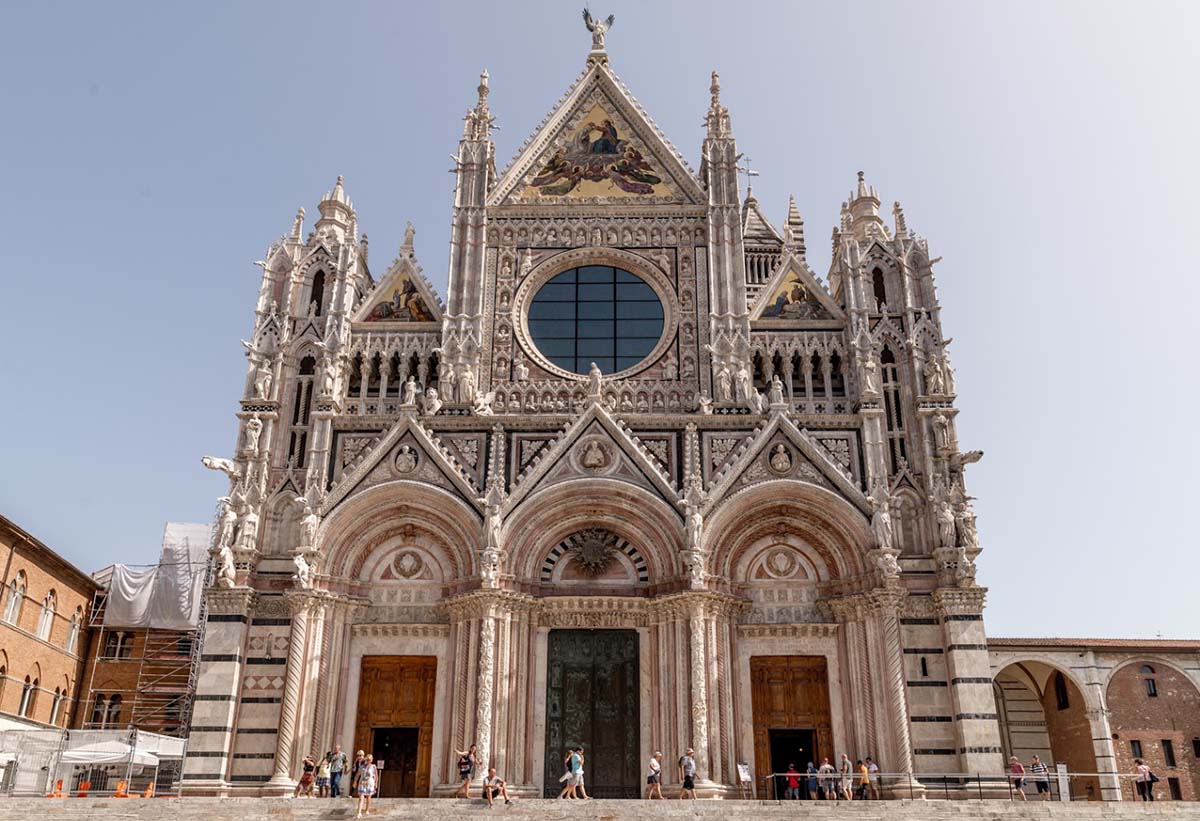












 Prepare to be amazed as the Wow Factor will captivate your senses the moment you enter the doors of this historic Gothic Cathedral. The black and white marble stripes on the walls and columns immediately captivate the eye. Black and white is seen throughout Siena and are the city’s symbolic colors.
Prepare to be amazed as the Wow Factor will captivate your senses the moment you enter the doors of this historic Gothic Cathedral. The black and white marble stripes on the walls and columns immediately captivate the eye. Black and white is seen throughout Siena and are the city’s symbolic colors.
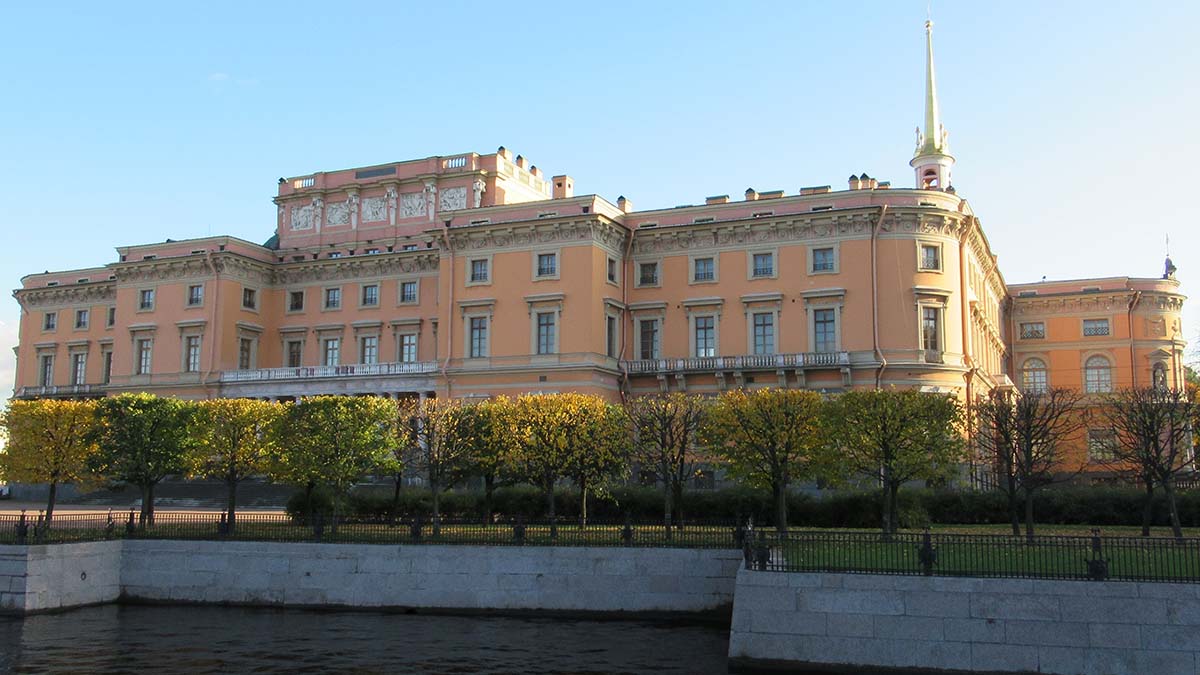





 I found Raskolnikov’s house, a big yellow apartment building, on the corner of Stolyarny Lane, 5, and Grazhdanskaya Street, 19. This rectangular structure with an inner yard has been built according to a typical architectural design of the 19th century: since the land was expensive, architects had to create the biggest possible house to occupy the lot. In 1970s, after remodeling, this “high, five-storied house” described by Dostoyevsky was turned into a four-storied one. [5] However, there is still the loft where Raskolnikov rented a room: “It was a tiny cupboard of a room about six paces in length … and it was so low-pitched that a man of more than average height … felt every moment that he would knock his head against the ceiling.” [6] The entrance to the house is locked to prevent tourists and literary journeys’ lovers, like myself, from disturbing the tenants.
I found Raskolnikov’s house, a big yellow apartment building, on the corner of Stolyarny Lane, 5, and Grazhdanskaya Street, 19. This rectangular structure with an inner yard has been built according to a typical architectural design of the 19th century: since the land was expensive, architects had to create the biggest possible house to occupy the lot. In 1970s, after remodeling, this “high, five-storied house” described by Dostoyevsky was turned into a four-storied one. [5] However, there is still the loft where Raskolnikov rented a room: “It was a tiny cupboard of a room about six paces in length … and it was so low-pitched that a man of more than average height … felt every moment that he would knock his head against the ceiling.” [6] The entrance to the house is locked to prevent tourists and literary journeys’ lovers, like myself, from disturbing the tenants. As I walked around the house, I saw the commemorative high relief of Dostoyevsky and the plaque with the inscription: “Raskolnikov’s House. The tragic lives of people of this neighborhood of Petersburg served for Dostoyevsky as a foundation of his passionate sermon of goodness for the entire humanity.” [7] There is an interesting tradition in St. Petersburg: on the first Saturday of July (events described in Crime and Punishment happened in the beginning of July), Dostoyevsky’s enthusiasts gather in this neighborhood to celebrate Dostoyevsky Day. Many bring flowers to place at the bottom of this relief, but some put here … axes, because Raskolnikov used an axe as his murder weapon. (Another reason for tenants of this house to keep the entrance door locked!)
As I walked around the house, I saw the commemorative high relief of Dostoyevsky and the plaque with the inscription: “Raskolnikov’s House. The tragic lives of people of this neighborhood of Petersburg served for Dostoyevsky as a foundation of his passionate sermon of goodness for the entire humanity.” [7] There is an interesting tradition in St. Petersburg: on the first Saturday of July (events described in Crime and Punishment happened in the beginning of July), Dostoyevsky’s enthusiasts gather in this neighborhood to celebrate Dostoyevsky Day. Many bring flowers to place at the bottom of this relief, but some put here … axes, because Raskolnikov used an axe as his murder weapon. (Another reason for tenants of this house to keep the entrance door locked!) After having found the house of the murderer, I need to find the house of his victim, an old woman, a notorious pawnbroker Alyona Ivanovna. The book presented her dwelling place as “a huge house which on one side looked on to the canal, and on the other into the street.” [8] The building fitting this description is located on the Griboedov Canal Quay, 104: one long side stretches along the Griboedov Canal, another – along Srednyaya Podyacheskaya Street, and the short side looks into Rimsky-Korsakov Street. Dostoyevsky gave another key for locating the old woman’s house – the number of steps that Raskolnikov made while walking there: “He had not far to go; he knew indeed how many steps it was from the gate of his lodging house: exactly seven hundred and thirty.” [9] Dostoyevsky, as a military engineer, was used to measuring distances in steps, and, knowing his obsession with precise details, we can presume that the writer gave us the correct number of steps.
After having found the house of the murderer, I need to find the house of his victim, an old woman, a notorious pawnbroker Alyona Ivanovna. The book presented her dwelling place as “a huge house which on one side looked on to the canal, and on the other into the street.” [8] The building fitting this description is located on the Griboedov Canal Quay, 104: one long side stretches along the Griboedov Canal, another – along Srednyaya Podyacheskaya Street, and the short side looks into Rimsky-Korsakov Street. Dostoyevsky gave another key for locating the old woman’s house – the number of steps that Raskolnikov made while walking there: “He had not far to go; he knew indeed how many steps it was from the gate of his lodging house: exactly seven hundred and thirty.” [9] Dostoyevsky, as a military engineer, was used to measuring distances in steps, and, knowing his obsession with precise details, we can presume that the writer gave us the correct number of steps. Now I had to take the subway to reach the Dostoyevsky Museum located on Kuznechny Lane, 5. Dostoyevsky rented twice apartments in this building: in 1846, at the beginning of his literary career, and in 1878, three years before his death. The main attraction of the museum is Dostoyevsky’s cabinet where he had written his novel Karamazov Brothers. On the massive desk there is an issue of the magazine, Russky Vestnik, with an extract from Karamazov Brothers, Dostoyevsky’s letters, and one of his favorite novels, Eugene Onegin by Alexander Pushkin. Everything on the table is at the particular place because the writer “paid a great attention to this pedantic order” [13]. There are two candlesticks with candles because Dostoyevsky disliked table lamps and preferred to write by candlelight. Since the writer worked a lot, being constantly in dire need for money because of his gambling problem, he often slept in his cabinet on the sofa. Above the sofa there is a reproduction of Dostoyevsky’s favorite picture, “The Sistine Madonna” by Raphael, presented by Sofia Tolstoy (Leo Tolstoy’s wife). Anna, Dostoyevsky’s widow, wrote: “How many times, during the last year of Fyodor Mikhailovich’s life, I found him standing in front of this great picture in such a deep adoration that he did not hear how I had entered.” [14] On February 9, 1881, Dostoyevsky died on the sofa in his cabinet.
Now I had to take the subway to reach the Dostoyevsky Museum located on Kuznechny Lane, 5. Dostoyevsky rented twice apartments in this building: in 1846, at the beginning of his literary career, and in 1878, three years before his death. The main attraction of the museum is Dostoyevsky’s cabinet where he had written his novel Karamazov Brothers. On the massive desk there is an issue of the magazine, Russky Vestnik, with an extract from Karamazov Brothers, Dostoyevsky’s letters, and one of his favorite novels, Eugene Onegin by Alexander Pushkin. Everything on the table is at the particular place because the writer “paid a great attention to this pedantic order” [13]. There are two candlesticks with candles because Dostoyevsky disliked table lamps and preferred to write by candlelight. Since the writer worked a lot, being constantly in dire need for money because of his gambling problem, he often slept in his cabinet on the sofa. Above the sofa there is a reproduction of Dostoyevsky’s favorite picture, “The Sistine Madonna” by Raphael, presented by Sofia Tolstoy (Leo Tolstoy’s wife). Anna, Dostoyevsky’s widow, wrote: “How many times, during the last year of Fyodor Mikhailovich’s life, I found him standing in front of this great picture in such a deep adoration that he did not hear how I had entered.” [14] On February 9, 1881, Dostoyevsky died on the sofa in his cabinet. Dostoyevsky was buried at one of the most famous cemeteries of St. Petersburg – the Tikhvin Cemetery at the Alexander Nevsky Monastery. The tombstone consists of the Orthodox cross and Dostoyevsky’s bust placed on two books. The cross is adorned by a garland of thorns symbolizing the writer’s sacrifices and hardships. The bust bears a resemblance to the writer because Dostoyevsky’s death mask was used for its creation. Two books, representing two parts of the Bible, symbolize his devotion to the Russian Orthodox Church; additionally, books symbolize his literary career. The tombstone’s inscription in Old Church Slavonic language is a quote from John 12:24: “…unless a grain of wheat falls into the ground and dies, it remains alone; but if it dies, it produces much grain.” This tomb is one of the most visited, and it is often adorned with fresh flowers.
Dostoyevsky was buried at one of the most famous cemeteries of St. Petersburg – the Tikhvin Cemetery at the Alexander Nevsky Monastery. The tombstone consists of the Orthodox cross and Dostoyevsky’s bust placed on two books. The cross is adorned by a garland of thorns symbolizing the writer’s sacrifices and hardships. The bust bears a resemblance to the writer because Dostoyevsky’s death mask was used for its creation. Two books, representing two parts of the Bible, symbolize his devotion to the Russian Orthodox Church; additionally, books symbolize his literary career. The tombstone’s inscription in Old Church Slavonic language is a quote from John 12:24: “…unless a grain of wheat falls into the ground and dies, it remains alone; but if it dies, it produces much grain.” This tomb is one of the most visited, and it is often adorned with fresh flowers.